What is 7-Hydroxymitragynine and Its Relation to Kratom

Faust
Kratom has captured global attention for its complex chemical makeup and diverse effects. At the heart of its properties lies 7-hydroxymitragynine, a compound that plays a pivotal role in shaping kratom’s unique characteristics. Unlike mitragynine, kratom’s most abundant alkaloid, 7-hydroxymitragynine is present in smaller quantities but carries significant influence. This blog post explores what this alkaloid is, how it relates to kratom, and why it matters to those interested in plant-based compounds. By diving into its chemistry, origins, and effects, we aim to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding for enthusiasts and newcomers alike.
Understanding 7-Hydroxymitragynine: The Basics
7-Hydroxymitragynine is an alkaloid found in the leaves of the kratom tree, scientifically known as Mitragyna speciosa. Alkaloids are naturally occurring compounds that often have pronounced physiological effects on humans. While kratom contains over 40 alkaloids, 7-hydroxymitragynine stands out due to its potency and distinct interactions within the body. It is a derivative of mitragynine, formed through a process called oxidation, where mitragynine is chemically altered to produce this more potent compound.
The kratom tree thrives in the humid, tropical climates of countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. For centuries, indigenous communities in these regions have chewed kratom leaves or brewed them into teas, valuing their ability to enhance energy, relieve discomfort, and promote relaxation. While mitragynine dominates in quantity, often making up 1-2% of the leaf’s dry weight, 7-hydroxymitragynine typically constitutes less than 0.2%. Despite its lower concentration, its effects are far-reaching, making it a focal point for those studying kratom’s chemistry.
The Chemistry Behind 7-Hydroxymitragynine
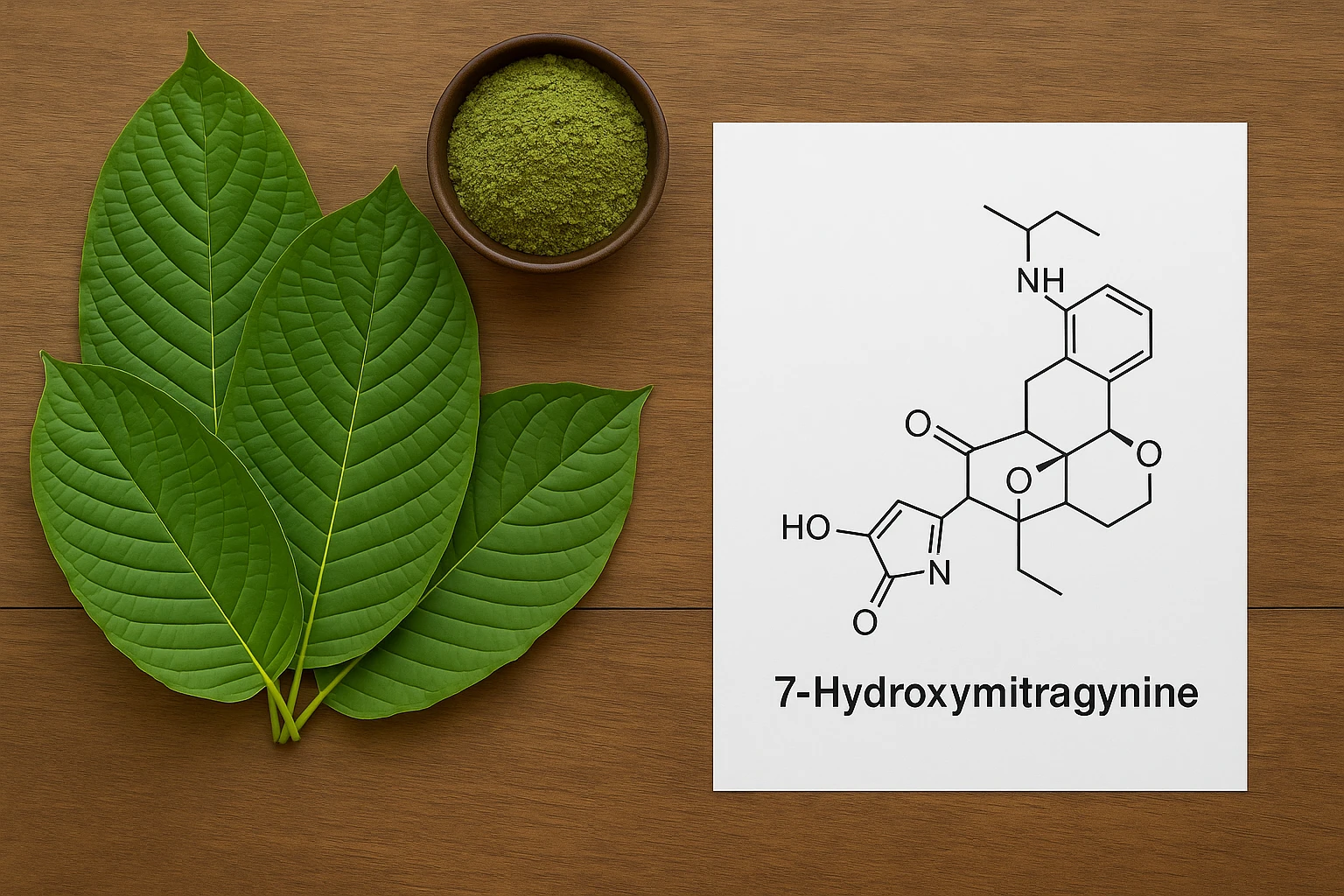
To grasp the significance of the chemistry of 7-hydroxymitragynine, it’s helpful to understand its chemical structure. As a derivative of mitragynine, it shares a similar molecular framework but includes a hydroxyl group (an oxygen and hydrogen atom pair) at the seventh position of its structure. This small modification dramatically enhances its ability to interact with certain receptors in the brain, contributing to its distinct effects.
The presence in kratom leaves is not solely dependent on the plant’s natural production. Environmental factors, such as soil quality, sunlight, and harvest timing, can influence alkaloid content. Additionally, post-harvest processing, like drying or fermentation, can increase the concentration of 7-hydroxymitragynine by converting mitragynine into its hydroxylated form. This variability explains why different kratom strains or batches may produce varying effects, even when sourced from the same region.

How 7-Hydroxymitragynine Works in the Body
The effects of 7-hydroxymitragynine stem from its interaction with the body’s opioid receptors, which are part of the central nervous system. These receptors regulate sensations like pain, mood, and relaxation. Unlike mitragynine, which has a broader range of receptor interactions, 7-hydroxymitragynine has a stronger affinity for specific opioid receptors, particularly the mu-opioid receptors. This targeted binding contributes to its potency, even at low concentrations.
When consumed, kratom’s alkaloids cross the blood-brain barrier and influence these receptors. Users often report feelings of calm, reduced discomfort, or mild euphoria, depending on the dose and strain. The compound’s effects are dose-dependent, meaning small amounts may produce stimulating effects, while larger amounts lean toward sedation. This dual nature is one of kratom’s hallmarks, and 7-hydroxymitragynine plays a key role in shaping these outcomes.
It’s important to note that while this alkaloid interacts with opioid receptors, its mechanism differs from traditional opioids. It acts as a partial agonist, meaning it activates receptors to a lesser degree than full agonists like morphine. This partial activation may explain why kratom’s effects are often described as milder and less habit-forming, though individual responses vary widely.
The Role of 7-Hydroxymitragynine in Kratom Strains
Kratom is commonly categorized into strains based on vein colour (red, green, white) or region of origin (e.g., Borneo, Maeng Da). These distinctions reflect differences in alkaloid profiles, including the concentration of 7-hydroxymitragynine. For example, red-vein strains, often associated with relaxation, may contain higher levels of 7-hydroxymitragynine due to specific growing conditions or processing methods. In contrast, white-vein strains, linked to energy and focus, may prioritize mitragynine.
The interplay between 7-hydroxymitragynine and other alkaloids creates what’s known as the entourage effect. This phenomenon suggests that kratom’s compounds work synergistically, producing effects that are greater than the sum of their parts. While 7-hydroxymitragynine is a key player, its impact is amplified by the presence of mitragynine, paynantheine, and other alkaloids. This complexity makes kratom a unique botanical, as no single compound fully accounts for its effects.
Origins and Cultural Context
The story of this alkaloid is inseparable from kratom’s cultural roots. In Southeast Asia, kratom has been a staple in traditional practices for generations. Farmers and labourers used it to combat fatigue during long workdays, while others turned to it for its calming properties. The discovery of 7-hydroxymitragynine, however, is a relatively recent development, driven by modern scientific interest in kratom’s chemistry.
Researchers began isolating kratom’s alkaloids in the 20th century, with 7-hydroxymitragynine identified in the 1990s. Its discovery shed light on why certain kratom preparations were more potent than others, sparking curiosity about its potential applications. Today, as kratom gains popularity worldwide, 7-hydroxymitragynine remains a focal point for those seeking to understand the plant’s effects and variability.

Factors Influencing 7-Hydroxymitragynine Content
The concentration of 7-hydroxymitragynine in kratom is not fixed and can vary based on several factors. These include:
- Growing Conditions: Soil pH, rainfall, and sunlight exposure affect alkaloid production. Trees grown in nutrient-rich environments may produce leaves with higher alkaloid content.
- Harvest Timing: Younger leaves tend to have different alkaloid ratios than mature ones. Farmers often time harvests to optimize desired compounds.
- Processing Techniques: Drying methods, such as sun-drying or indoor drying, can alter alkaloid profiles. Fermentation, a common practice for red-vein strains, may increase their levels by promoting oxidation.
- Storage: Improper storage, such as exposure to heat or moisture, can degrade alkaloids over time, reducing the potency of this alkaloid.
These variables highlight the importance of sourcing kratom from reputable suppliers who prioritize quality control. For users, understanding these factors can help explain why one batch of kratom feels different from another.
Why 7-Hydroxymitragynine Matters
The significance of 7-hydroxymitragynine extends beyond its chemical properties. For kratom users, it represents a key factor in the plant’s versatility. Whether someone seeks energy, calm, or relief, the presence of this alkaloid shapes the experience. Its potency also raises questions about responsible use, as higher concentrations may amplify effects and influence individual responses.
For researchers, 7-hydroxymitragynine offers a window into kratom’s potential. Its interactions with opioid receptors have sparked interest in its pharmacological properties, though much remains to be explored. As kratom continues to gain traction globally, understanding compounds like 7-hydroxymitragynine will be crucial for ensuring safe and informed use.
The Future of 7-Hydroxymitragynine Research
As interest in kratom grows, so does the focus on 7-hydroxymitragynine. Scientists are keen to explore its pharmacological potential, particularly its interactions with opioid receptors. While kratom remains controversial in some regions due to regulatory concerns, this compound offers opportunities for deeper understanding. Future research may clarify its role in kratom’s effects and shed light on its safety profile.
For now, 7-hydroxymitragynine remains a fascinating piece of the kratom puzzle. Its potency, variability, and synergy with other alkaloids make it a compound worth understanding for anyone interested in plant-based remedies.

FAQ: 7-Hydroxymitragynine and Its Relation to Kratom
Q: What exactly is 7-hydroxymitragynine?
A: 7-Hydroxymitragynine is an alkaloid found in kratom leaves (Mitragyna speciosa). It’s a derivative of mitragynine, formed through oxidation, and is known for its potent effects despite being present in small amounts (less than 0.2% of the leaf’s dry weight). It contributes significantly to kratom’s unique properties, such as relaxation and discomfort relief.
Q: How does 7-hydroxymitragynine differ from mitragynine?
A: While both are alkaloids in kratom, 7-hydroxymitragynine is less abundant but more potent than mitragynine. It has a stronger affinity for mu-opioid receptors, leading to more pronounced relaxation effects. Mitragynine, present in higher quantities (1-2%), is often linked to stimulation at lower doses and interacts with a broader range of receptors.
Q: Why is 7-hydroxymitragynine important in kratom?
A: 7-Hydroxymitragynine is key to kratom’s effects due to its potency and interaction with opioid receptors. It enhances sensations like calm and relief, particularly in strains like red-vein kratom. Its synergy with other alkaloids creates the plant’s versatile effects, making it a focal point for understanding kratom’s potential.
Q: Does the amount of 7-hydroxymitragynine vary in different kratom strains?
A: Yes, the concentration of 7-hydroxymitragynine varies across strains due to factors like growing conditions, harvest timing, and processing methods. Red-vein strains, often processed through fermentation, may have higher levels, contributing to their relaxing effects, while white-vein strains typically prioritize mitragynine for energy.
Q: How does 7-hydroxymitragynine affect the body?
A: 7-Hydroxymitragynine interacts with mu-opioid receptors in the brain, influencing sensations like pain, mood, and relaxation. As a partial agonist, it activates these receptors less intensely than traditional opioids, leading to milder effects that can range from stimulation at low doses to sedation at higher doses.
Q: Can processing methods increase 7-hydroxymitragynine in kratom?
A: Yes, certain processing techniques, like fermentation or specific drying methods, can increase their levels by converting mitragynine into its hydroxylated form through oxidation. This is why some kratom batches, particularly red-vein varieties, may feel more potent.
Q: How was 7-hydroxymitragynine discovered?
A: 7-Hydroxymitragynine was identified in the 1990s as researchers studied kratom’s alkaloids. Its discovery helped explain the potency of certain kratom preparations, building on earlier work isolating mitragynine and other compounds in the 20th century.
Conclusion
7-Hydroxymitragynine is a cornerstone of kratom’s complex chemistry, offering insight into why this plant has captivated users for centuries. From its origins in Southeast Asia to its role in modern kratom strains, this alkaloid shapes the plant’s effects in profound ways. By interacting with opioid receptors, it contributes to sensations of calm, relief, and relaxation, while its synergy with other compounds creates kratom’s signature versatility.
For enthusiasts, understanding how this alkaloid unlocks a deeper appreciation of kratom’s potential. As research evolves, this compound will likely remain at the forefront of discussions about kratom’s place in the world of plant medicine.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog about 7-hydroxymitragynine and kratom is intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) and its alkaloids have not been fully evaluated by regulatory authorities such as Health Canada for safety or efficacy.
The effects of kratom can vary widely based on dosage, strain, individual physiology, and other factors, and its use may carry risks, including potential side effects, interactions with medications, or dependency with prolonged use. Individuals considering kratom should consult a qualified healthcare professional before use, especially those with pre-existing medical conditions, who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or who are taking other medications.
The authors and publishers of this blog are not responsible for any adverse effects or consequences resulting from the use of kratom or reliance on the information presented. Always source kratom from reputable vendors and adhere to local laws and regulations regarding its use.